Temple of Edfu, also known as the Temple of Horus, is a magnificent archaeological site that stands as a testament to the grandeur of ancient Egyptian civilization. Situated on the west bank of the Nile River, near Edfu in Upper Egypt, this temple holds immense historical and cultural significance. With its rich architectural features, captivating mythology, and deep-rooted traditions, the Temple of Edfu offers visitors a captivating journey into the past worldwide.
The Temple of Edfu Significance
The Temple of Edfu is located approximately halfway between Luxor and Aswan, two prominent cities in Egypt. Its strategic position highlights its significance as a religious center during the Ptolemaic period, which lasted from 305 BCE to 30 BCE. Built on the site of a much older shrine dedicated to Horus, the temple is dedicated to the falcon-headed god, Horus, the divine protector of Egypt’s kings.
The construction of the Temple of Edfu began in the reign of Ptolemy III in the 3rd century BCE and was completed two centuries later during the reign of Ptolemy XII. The temple played a crucial role in ancient Egypt’s religious and political life, symbolizing the divine power of Horus and honoring the Ptolemaic rulers who considered themselves as the pharaohs’ legitimate successors.
Architectural Features
1. Exterior
-
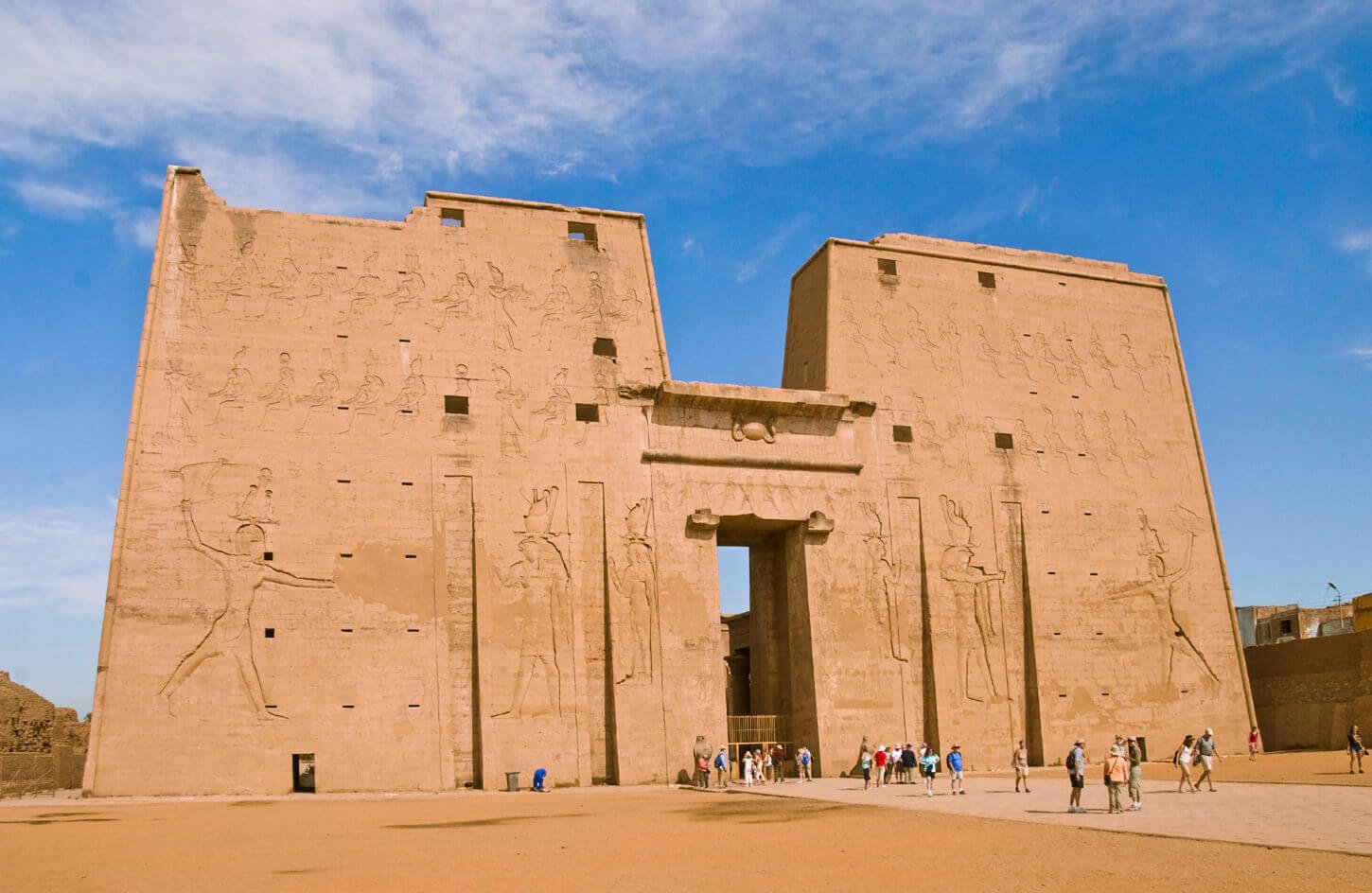
Entrance and pylons: The entrance to the Temple of Edfu is marked by colossal sandstone pylons and towering gateways that lead into the temple complex. Adorned with intricate reliefs and inscriptions, these pylons serve as majestic guardians, inviting visitors into the world of ancient Egyptian religious devotion.
-
Courtyard and colonnade: Beyond the entrance, visitors step into a spacious courtyard surrounded by a colonnade of beautifully carved columns. The courtyard was once bustling with religious processions and ceremonies, and its architectural splendor reflects the grandeur of the Ptolemaic era.
-
Hypostyle Hall: Passing through the courtyard, visitors enter the awe-inspiring Hypostyle Hall, a vast columned hall with towering pillars adorned with ornate capitals. The hall’s ceiling is decorated with celestial scenes and religious motifs, transporting visitors into a realm where gods and mortals commune.
2. Interior
-
Sanctuaries: The inner sanctuaries of the Temple of Edfu are dedicated to various deities, with the central sanctuary housing the statue of Horus. The sanctuaries were considered the holiest areas of the temple, accessible only to high-ranking priests. Elaborate rituals and offerings took place within these sacred spaces.
-
Offering Halls: Adjacent to the sanctuaries are the offering halls, where priests conducted daily rituals and presented offerings to the gods. The walls of these halls are adorned with reliefs depicting scenes of worship and mythological narratives, providing glimpses into ancient Egyptian religious practices.
-
Chapels: Several small chapels can be found throughout the temple complex, each dedicated to a specific deity or purpose. These intimate spaces were used for private worship, providing devotees a more personal connection to the divine.

History and Mythology
Construction and dedication
The Temple of Edfu was constructed to honor the falcon-headed god, Horus, to commemorate his victory over Seth, the god of chaos and disorder. The temple’s dedication and construction were part of the mythological narrative of Horus seeking revenge for the murder of his father, Osiris.
Worshipping deities
While dedicated primarily to Horus, the Temple of Edfu also paid homage to other deities associated with the mythological narrative, including Hathor, the goddess of love and joy, and Harsomptus, the son of Horus and Hathor. The temple served as a center for the worship of these gods, attracting pilgrims from far and wide.
Restoration and preservation efforts
Over the centuries, the Temple of Edfu gradually deteriorated due to natural elements and human activities. However, extensive restoration projects have been undertaken to preserve its architectural splendor and cultural significance. These efforts have helped to protect the temple’s intricate reliefs, vibrant colors, and monumental structures, ensuring that future generations can appreciate its beauty.
Rituals and Festivals
Daily temple rituals
The Temple of Edfu was the focal point for various daily rituals conducted by the temple priests. These rituals included purification ceremonies, offerings, and prayers to invoke the blessings of the gods and maintain harmony between the mortal and divine realms.
Major festivals and processions
-
Festival of Horus: The Temple of Edfu hosted an annual festival known as the Festival of Horus, a grand celebration that lasted for several weeks. The festival involved processions, dramatic reenactments of mythological events, and vibrant performances to honor Horus and his triumph over Seth.
-
Opet Festival: During the Opet Festival, one of the most significant religious events in ancient Egypt, the statues of Horus, his consort Hathor, and their son Harsomptus were carried in a ceremonial procession from the Temple of Karnak in Luxor to the Temple of Edfu. The procession attracted pilgrims from all over the country and showcased the importance of Edfu as a religious center.

Symbolism and Iconography
Depictions of gods and pharaohs
The Temple of Edfu is adorned with intricate reliefs and carvings depicting gods, pharaohs, and various mythological scenes. These artistic representations provide valuable insights into ancient Egypt’s religious beliefs, royal propaganda, and societal norms.
Mythological scenes and narratives
The temple’s walls and columns depict mythological narratives, including the battles between Horus and Seth, the divine birth of Harsomptus, and the journey of Horus to avenge his father’s death. These scenes served both a religious and educational purpose, reinforcing the power of the gods and the importance of maintaining Ma’at, the cosmic order.
Hieroglyphic inscriptions
Hieroglyphic inscriptions covering the temple’s walls and surfaces provide information about the ancient Egyptian language, religious rituals, and historical events. Decoding these inscriptions has been instrumental in unraveling the mysteries of ancient Egypt and expanding our understanding of its culture.
Cultural and Historical Significance
Religious importance
The Temple of Edfu held immense religious significance as a center for worship and pilgrimage. It served as a place for devotees to connect with the gods, seek divine blessings, and partake in rituals believed to ensure the prosperity and well-being of the pharaoh and the entire kingdom.
Architectural and artistic achievements
The temple’s architectural design, with its towering pylons, massive colonnades, and intricate reliefs, showcases the remarkable achievements of ancient Egyptian architecture. The precision and skill of the artisans who crafted the temple’s decorations and inscriptions are a testament to the advanced craftsmanship of the time.
Insights into Ancient Egyptian Civilization
The Temple of Edfu offers valuable insights into ancient Egypt’s religious beliefs, social structures, and daily life. From the portrayal of gods and pharaohs to scenes of agricultural practices and mythological narratives, the temple provides a window into this ancient civilization’s cultural and historical context.
Tourism and Visitor Experience
Accessibility and visitor facilities
The Temple of Edfu is easily accessible for tourists, with well-maintained paths and informative signage guiding visitors through the complex. Visitor facilities, including visitor centers, rest areas, and guided tour services, enhance the overall experience.
Highlights and notable attractions
Visitors to the Temple of Edfu can marvel at the well-preserved reliefs and carvings that adorn the temple’s walls, experiencing the grandeur of ancient Egyptian art and architecture firsthand. The Hypostyle hall, with its towering columns and celestial scenes, is a particular highlight that leaves visitors in awe.
Impact on local economy and community
The Temple of Edfu plays a significant role in the local economy, attracting tourists and providing employment opportunities for the surrounding communities. The revenue generated from tourism helps support local businesses, infrastructure development, and cultural preservation efforts.
Conservation Challenges and Efforts
Environmental threats
The Temple of Edfu faces environmental challenges, including exposure to sun, wind, and sand erosion. Climate change and rising groundwater levels also threaten the temple’s structural stability and preservation.
Conservation projects and initiatives
To safeguard the temple for future generations, ongoing conservation projects focus on monitoring and addressing environmental risks and implementing careful cleaning and restoration techniques. Collaborative efforts between local authorities, international organizations, and experts in Egyptology are crucial in preserving the temple’s integrity.
Temple of Edfu’s significance
The Temple of Edfu is a magnificent testament to ancient Egyptian architecture, religious devotion, and mythological narratives. Its rich history, beautiful symbolism, and cultural importance make it a must-visit destination for travelers seeking to delve into the wonders of ancient Egypt.
With ongoing preservation efforts and increased awareness of its historical value, the Temple of Edfu is poised to continue enchanting visitors and researchers alike. By immersing ourselves in its grandeur, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the achievements of ancient Egyptian civilization and the enduring legacy it has left behind.
Related Articles You Might Find Interesting:

0 Comment