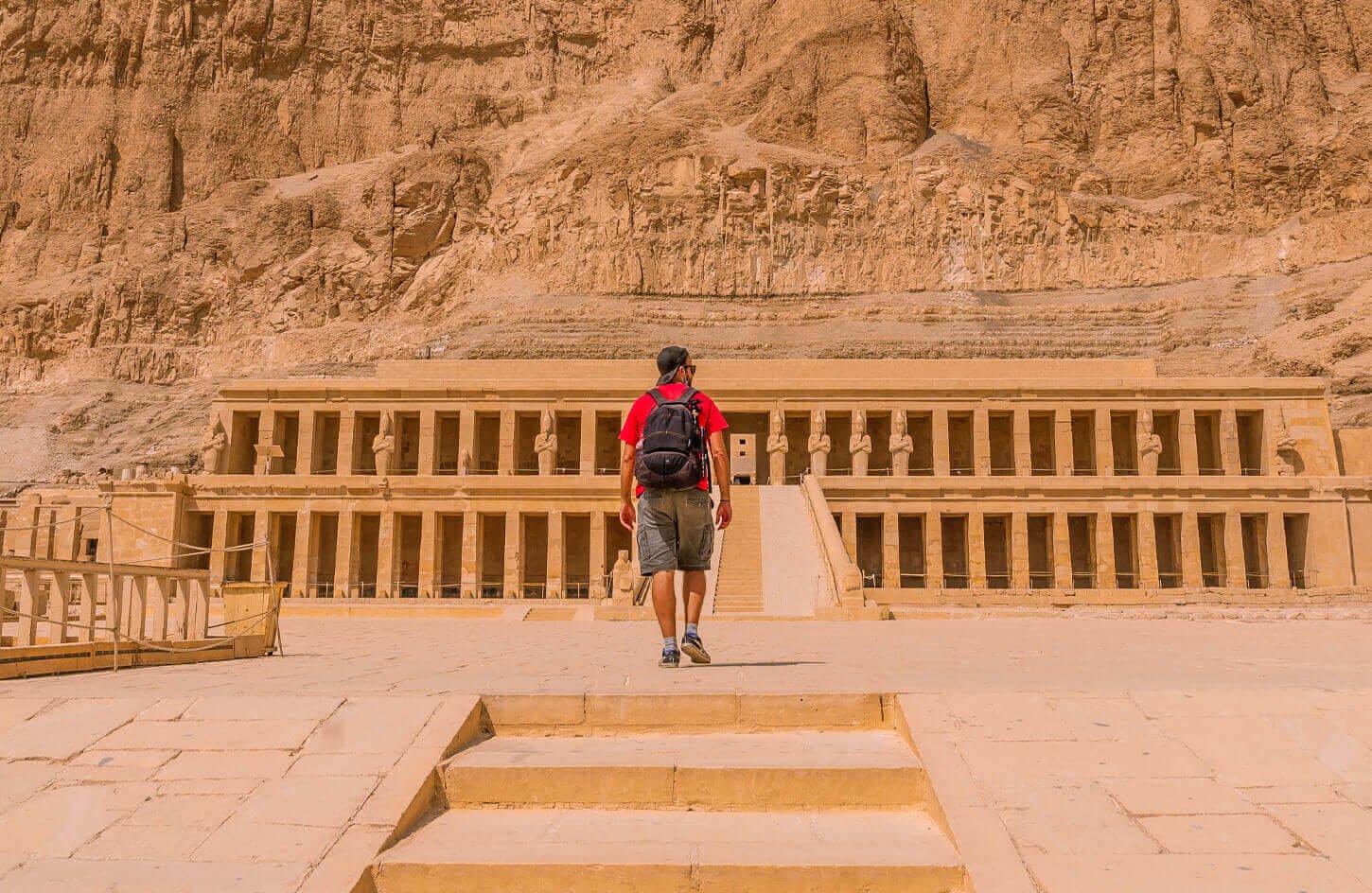
The Temple of Hatshepsut is a majestic testament to the greatness of one of ancient Egypt’s most great pharaohs. Nestled within the rugged cliffs of Deir el-Bahari, near Luxor, this magnificent mortuary temple draws visitors worldwide.
With its rich historical significance and awe-inspiring architectural features, the Queen Hatshepsut Temple offers a captivating journey into the past, allowing us to unravel the extraordinary life and reign of Queen Hatshepsut.
Overview of the Temple of Hatshepsut and Significance
Situated on the western bank of the Nile River, the Temple of Hatshepsut holds a commanding position in the landscape, surrounded by the natural grandeur of the Theban mountains.
This location was carefully chosen for its spiritual significance, as it represented the gateway to the afterlife. The temple’s strategic positioning and architectural splendor emphasize the importance of Hatshepsut’s legacy as a revered pharaoh of ancient Egypt.
Queen Hatshepsut and Her Reign
In the 15th century BCE, Hatshepsut ascended to the throne during the New Kingdom, a period characterized by Egypt’s military might and cultural prosperity. Her reign was unique, as she was one of the few female pharaohs in the history of ancient Egypt.
Hatshepsut’s unparalleled rise to power defied conventions and paved the way for her enduring legacy.

Historical Background
To appreciate the significance of the Temple of Queen Hatshepsut, it is essential to understand the broader historical context of the New Kingdom. This era marked a period of renaissance in Egypt, witnessing impressive advancements in art, architecture, and trade.
Amidst this vibrant era, Hatshepsut emerged as a visionary leader, consolidating her authority and bringing stability to the kingdom.
Hatshepsut’s Rise to Power and Unique Reign as a Female Pharaoh
Hatshepsut’s ascent to the throne was extraordinary, as women were typically relegated to supporting roles in the royal court. Undeterred by societal norms, she boldly assumed the title of pharaoh, proclaiming her divine birthright.
As a skilled administrator and diplomat, Hatshepsut’s reign ushered in an era of peace and prosperity, fostering trade relations and cultural exchange with neighboring lands.
Construction of the Temple as a Testament to Her Legacy
To immortalize her reign, Hatshepsut commissioned the construction of the Temple at Deir el-Bahari. Designed by the renowned Senenmut, the temple complex was a grand funerary monument dedicated to the goddess Hathor and the revered Amun-Ra. Its magnificence was intended to celebrate Hatshepsut’s achievements and assert her authority as a legitimate pharaoh.
Architectural Features
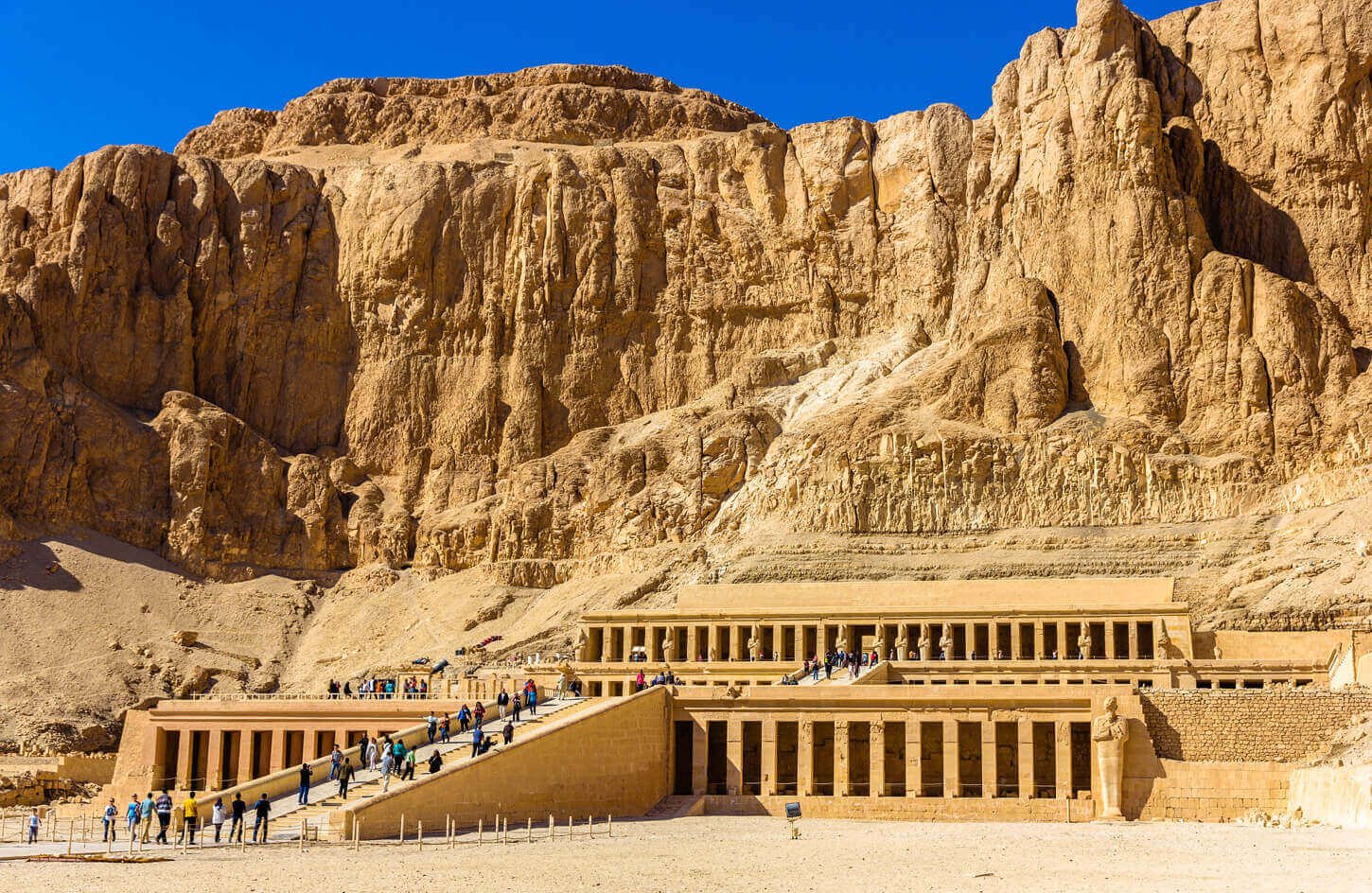
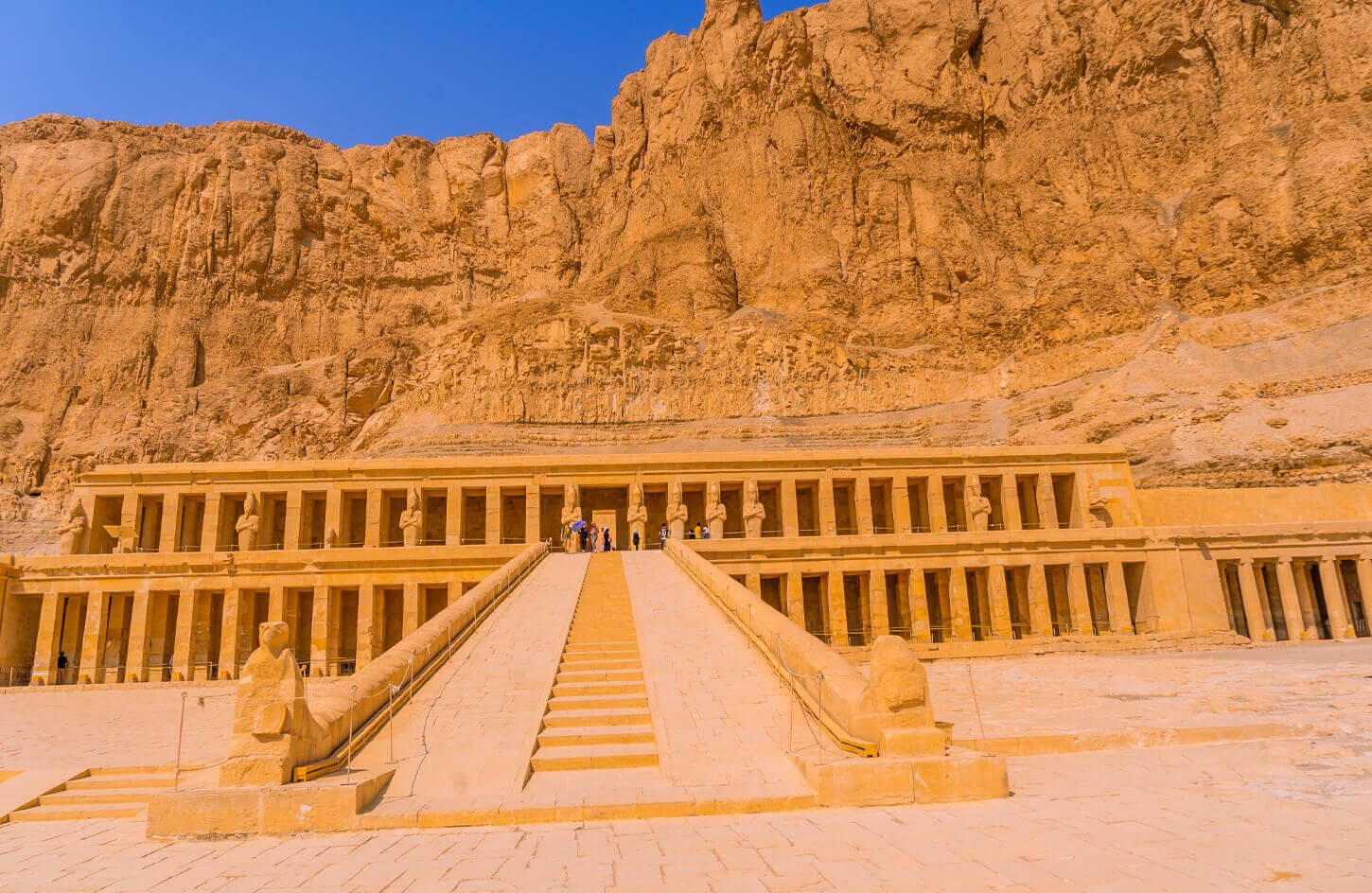
The Temple of Hatshepsut is a masterpiece of ancient Egyptian architecture, boasting a harmonious blend of natural surroundings and man-made structures. Its design encompasses three main tiers, connected by terraces and colonnaded porticoes, each showcasing remarkable craftsmanship and symbolic significance.
General Layout and Design of the Temple
The temple’s layout adheres to traditional Egyptian architecture, characterized by axial symmetry and precise alignments. It comprises several courtyards, terraces, and chapels, leading visitors on a carefully orchestrated journey of spiritual exploration.
The Three-Tiered Terraces and Their Purpose
Rising from the desert floor, the temple’s three-tiered terraces create a visually striking spectacle. Each level served a specific function, with the lower terrace dedicated to the Osirian cult, the middle terrace housing the chapels of various deities, and the upper terrace featuring divine rituals and ceremonial activities.
The Colonnaded Porticoes and Their Decoration
One of the defining features of the Temple of Hatshepsut is its elegant colonnaded porticoes. These grand corridors are adorned with intricate reliefs and vibrant murals depicting scenes from Hatshepsut’s life and religious ceremonies. The meticulous craftsmanship and attention to detail demonstrate the exceptional skill of ancient Egyptian artisans.

The Mortuary Temple Complex
Queen Hatshepsut Temple encompasses a vast mortuary complex that provides a sacred space for rituals and offerings to honor the queen’s spirit and ensure her eternal afterlife.
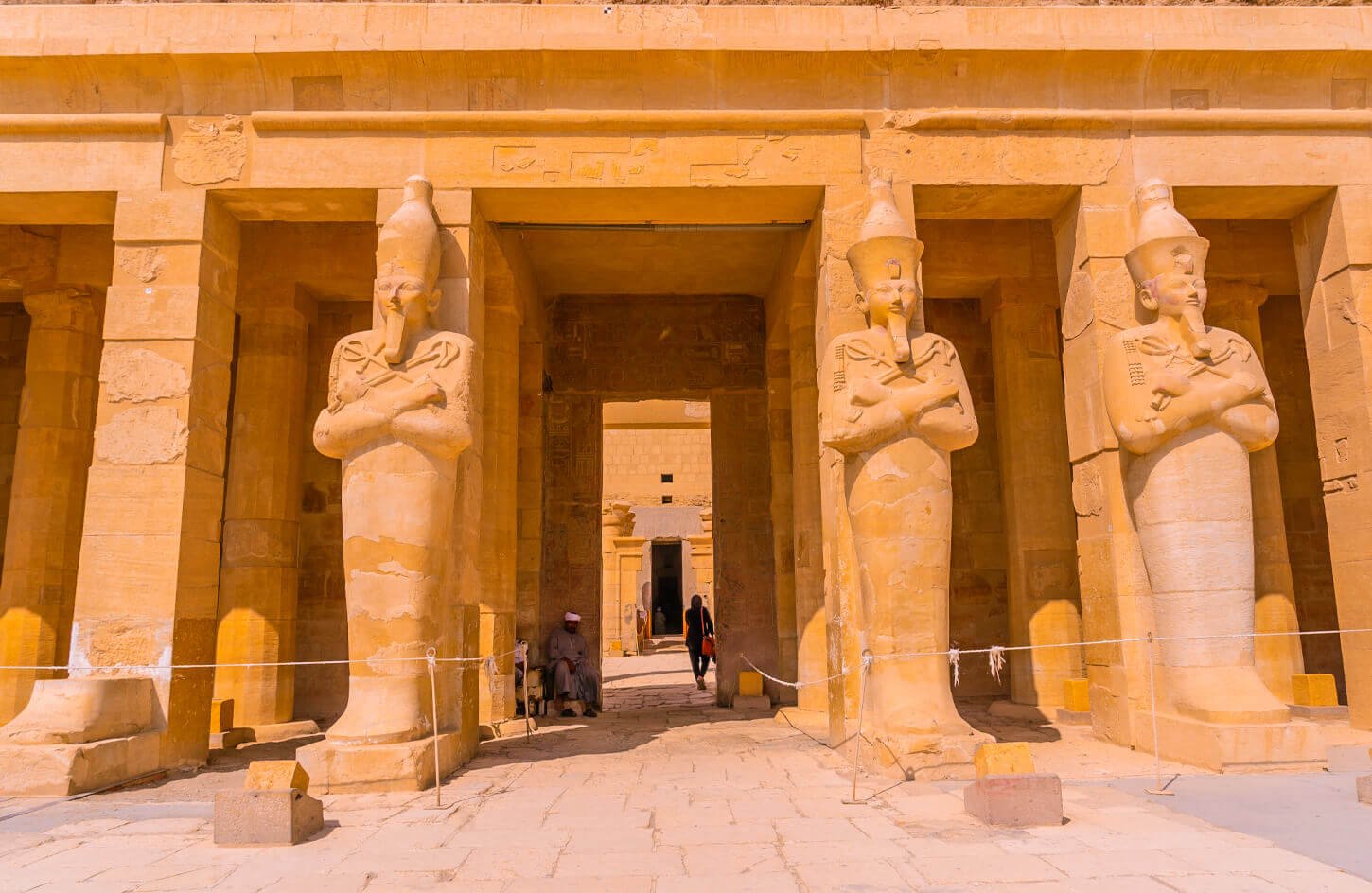
The Main Entrance and the Pylon
As visitors approach the temple, they pass through the towering pylon, an imposing gateway that symbolizes the boundary between the earthly realm and the sacred domain of the gods. Carved reliefs on the pylon walls depict victorious military campaigns and religious processions.
The Courtyard of the Cachettes
Beyond the pylon, the Courtyard of the Cachettes unfolds, showcasing magnificent statues of pharaohs and gods. This open space served as a gathering place for ceremonies and provided access to the main sanctuary.
The Sanctuary of Amun and Associated Chapels
At the heart of the temple complex lies the Sanctuary of Amun, where Hatshepsut’s burial chamber was. Surrounding this sacred space are numerous chapels dedicated to various deities, highlighting the queen’s devotion to the Egyptian pantheon.
The Birth Colonnade
Among the temple’s most outstanding features is the Birth Colonnade, which serves as a historical record and a testament to Hatshepsut’s divine birth and legitimacy as a pharaoh.
Description of the Reliefs and Their Significance
The walls of the Birth Colonnade are adorned with intricate reliefs that narrate the story of Hatshepsut’s divine conception and her divine mandate to rule. These reliefs celebrate her connection to the gods and convey her legitimacy as a ruler.
Depictions of Hatshepsut’s Divine Birth and Legitimacy as a Pharaoh
The reliefs vividly portray the mythological accounts of Hatshepsut’s birth, illustrating her divine lineage and association with powerful deities such as Amun-Ra. Hatshepsut solidified her claim to the throne through these depictions and reinforced her position as a legitimate pharaoh.
Religious and Mythological Scenes Portrayed in the Birth Colonnade
The Birth Colonnade also showcases religious and mythological scenes, capturing important rituals, offerings, and interactions with the gods. These scenes serve as a visual tribute to ancient Egypt’s religious beliefs and practices during Hatshepsut’s reign.

The Upper Terrace
Ascending to the upper terrace, visitors encounter additional chapels dedicated to different deities, showcasing the religious fervor and cultural significance that permeated the queen’s reign.
The Chapel of Anubis
The Chapel of Anubis, the jackal-headed god associated with mummification and the afterlife, represents a space of reverence and spiritual connection to the divine. Here, Hatshepsut sought protection and guidance for her journey to immortality.
The Hathor Chapel
Dedicated to the goddess Hathor, known as the divine mother and protector of the pharaohs, the Hathor Chapel features great reliefs and pillars adorned with Hathor’s iconic cow ears and sun disk. It served as a sanctuary for Hatshepsut to express her devotion to the deity.
The Chapel of the Royal Cult
The Chapel of the Royal Cult was a place of ceremonial worship and offerings to honor the pharaoh and ensure her eternal reign. Lavishly decorated, it exemplifies Hatshepsut’s efforts to secure her legacy as a powerful ruler.
The Lower Terrace
Visitors descend to the lower terrace and encounter the Osirian chapels and reliefs depicting Hatshepsut’s expedition to the land of Punt. This endeavor further solidified her reputation as a prosperous and ambitious pharaoh.
The Osirian Chapels
The Osirian chapels, dedicated to the god Osiris, served as a space for funerary rituals and offerings to honor Hatshepsut’s ancestors. These chapels reinforced her connection to the divine lineage and emphasized the eternal cycle of life and death.
The Punt Reliefs and Their Portrayal of Hatshepsut’s Expedition
Exquisite reliefs on the lower terrace walls depict the famous expedition to the land of Punt, where Hatshepsut sought exotic treasures, precious woods, and incense. These reliefs provide valuable insights into ancient Egyptian trade networks and cultural exchange during Hatshepsut’s reign.
Restoration and Excavation Efforts
Over the centuries, the Temple of Hatshepsut suffered from natural elements, human intervention, and the passage of time. However, extensive restoration and excavation efforts have been undertaken to preserve and uncover its grandeur.
The Temple’s Rediscovery in Modern Times
The temple complex was rediscovered in the 19th century and has become a focal point of archaeological exploration and preservation. Archaeologists have diligently pieced together fragments of the temple’s history, allowing us to appreciate its architectural marvels.
Conservation and Restoration Projects
Renowned preservation teams have carried out meticulous restoration projects to safeguard the temple’s structural integrity and conserve its intricate reliefs and artworks. These efforts ensure that future generations can marvel at the temple’s splendor.
Current State and Accessibility for Visitors
Today, the Temple of Hatshepsut stands as a captivating attraction, open to visitors who yearn to experience the grandeur of ancient Egypt. Accessible paths and informative signage guide visitors through its various sections, offering a glimpse into the rich tapestry of Hatshepsut’s life and the fascinating history of the New Kingdom.
Significance and Legacy
Hatshepsut’s impact on ancient Egyptian history cannot be overstated. Her reign marked a significant period of stability, cultural growth, and international relations. The Temple of Hatshepsut is a testament to her accomplishments, ensuring that her name and legacy endure through the ages.
The Temple of Hatshepsut as a Testament to Her Accomplishments
This remarkable temple complex is a testament to Hatshepsut’s vision, ambition, and devotion to the gods. Its grandeur reflects her immense contributions to Egyptian society and her unwavering commitment to her people’s prosperity and spiritual well-being.

Influence on Subsequent Architectural Styles and Royal Mortuary Temples
The architectural innovations and artistic expressions in the Temple of Queen Hatshepsut influenced later generations of builders and craftsmen. Elements of its design and decoration can be observed in subsequent Egyptian structures, leaving an indelible mark on the architectural heritage of ancient Egypt.
The Queen Hatshepsut Temple is an extraordinary archaeological marvel that provides a glimpse into the remarkable life and reign of one of ancient Egypt’s most influential pharaohs. Its architectural brilliance and historical significance make it a must-visit destination for those seeking to immerse themselves in the captivating world of ancient Egypt. As we explore its various sections and immerse ourselves in its timeless grandeur, we pay homage to the enduring legacy of Hatshepsut, a queen who defied societal norms and left an indelible mark on history.
Related Articles You Might Find Interesting:

0 Comment